
Pes cavus with an increased calcaneal inclination angle and talar–first metatarsal angle.

59– 60)Ĭlassification of pes cavus based on the dominant component of the deformity. Radiographic measurements in pes planovalgusĬalcaneal inclination angle (see pp. 1 = Plantar plane 2 = Longitudinal axis of talus 3 = Longitudinal axis of first metatarsal α = Talar declination angle (α = 47°) β = Talar–first metatarsal angle (β = – 26°) 1 = Plantar plane 2 = Line tangent to inferior border of calcaneus α = Calcaneal inclination angle (α = 15°) Pes planovalgus with an increased talar declination angle and abnormal (negative) talar–first metatarsal angle. Pes planovalgus with a decreased calcaneal inclination angle. Reference lines and angles used in evaluating pediatric foot deformities on dorsoplantar radiographs. Reference lines and angles used in evaluating pediatric foot deformities on lateral radiographs. Measuring techniques can be used to evaluate the different components of the deformity ( Table 4.3). Pes calcaneocavus is characterized by an increased vertical position of the heel. If the dominant features are inclination of the forefoot and associated toe deformities, the condition is classified as pes cavovarus. Subtypes are identified on the basis of clinical findings and the position of the hindfoot ( Figs. Pes cavus is a foot deformity in which the forefoot is fixed in plantar flexion, creating an abnormally high longitudinal arch. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 1965 93:374–381 Standardization of terminology and evaluation of osseous relationships in congenitally abnormal feet. Can Med Assoc J 1964 91:840–844 Templeton AW, McAlister WH, Zim ID. A radiographic analysis of major foot deformities. Huntington NY: Krieger Publishing 1975 Ritchie GW, Keim HA. Specific deformities, measurements, and diagnostic techniques are described more fully in the sections below.
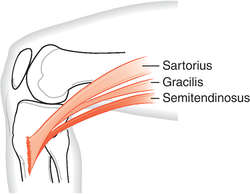
A common feature of all the studies is that the authors placed key emphasis on the evaluation of the hindfoot. 4.21 and 4.22review the diagnostic work-up of pediatric foot deformities based on three studies conducted in patients 0–12 years of age.
Overview of Pediatric and Congenital Foot Deformitiesĭescriptions of congenital and pediatric foot deformities vary widely in the literature, and varying techniques have been used in their radiographic measurement.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
